We are no longer talking about the mere fact of eliminating foreign substances from the skin but we also deal with combination treatments including disinfection, conditioning for follow-up treatments and the stimulation of regenerative processes in the skin. There is a long list of substances that find their way on our (facial) skin every day:
- Natural substances of the body: skin barrier components, skin cells, scabs, glandular secretions such as sebum, sweat, earwax, lacrimal fluid and saliva. Curiously enough, all these components belong to the self-cleansing programme of the skin.
- Natural environmental substances: mineral dusts (mineral clay, silicic acid, salts etc.), herbal substances (hydrocarbons, lipids, waxes, pollen etc.), peroxided hydrocarbons such as peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN).
- Reaction products of skin components with gases such as oxygen, ozone, nitrogen oxides, sulphur dioxide and chlorine.
- Anthropogenic substances: powders and aerosols (house-, street- and industrial dust including soot particles and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), working substances, household chemicals and fashion jewellery components (silver- and nickel compounds).
- Ingredients in skin care products: lipid substances, active agents, pigments (from lip sticks, makeup, camouflage, powders and mineral-based sun screens), dyes (mascara, eyeliner pencils) and various cosmetic additives.
- Microorganisms and their waste- and metabolic products including enzymes and fatty acids.
Types of applications
These substances can be water-, oil- respectively fat-soluble, completely insoluble or adhesive. These features are crucial for the selection of the cleansing product:
- Tensides in the form of soap bars, cleansing gels or oil-in-water-emulsions have a high dirt-absorbing capacity and usually are most appropriate to remove all kinds of substances.
- Micelle water is a gentle cleansing lotion also consisting of water and low concentrations of tensides. It can be compared with a drop of detergent and a lot of water in the kitchen.
- The term microemulsion is used as a technical name for highly concentrated, tenside-containing formulations in which tensides and water form a homogenous phase. Microemulsions often serve as a base for the preparation of shampoos.
- In the production of adhesive cosmetic products (makeups, camouflage) also short-chained oils (triglycerides, synthetic esters) are used which then are removed with aqueous tensides. An alternative are non-aqueous, tenside-containing oils that form emulsions on the skin after contact with water and thus can easily be removed (2-in-1-products).
- In cases of very sensitive skin and for the skin care of small children either native oils in pure form are suitable or emulsions with high oil content (cleansing milk). In case that the latter mentioned have a lamellar structure due to the hydrogenated phosphatidylcholine base (2-in-1-products, see below) they also are very appropriate skin care formulations. Cleansing milk can also be used for makeup removal.
Tensides & emulsifiers
Tensides, like emulsifiers, are surface-active substances, often with a similar chemical structure so that the terms practically are synonyms. If cleansing products are concerned, the term tenside generally is used whereas the term emulsifiers more often is applied in connection with skin care products. Both of them cause a washout effect which cannot be avoided in the context of cleansing products but is unwanted when skin care products are concerned. A distinguishing feature in terms of quality is the critical micelle concentration (CMC), a physical value informing on the concentration at which surface-active substances combine in water to form so-called assemblies.
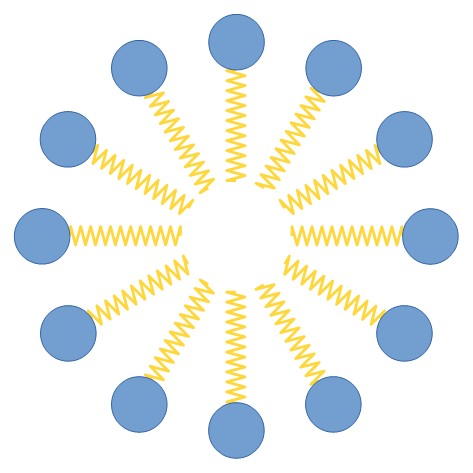
Micelle model;
the hydrophilic heads of tensides are oriented towards the water phase
while the lipophilic moieties are inbound.
Tensides tend to have a higher CMC. With increasing CMC the irritation potential also increases. That is the reason why cleansing products should only shortly remain on the skin and immediately be rinsed off (“rinse-off” products). In that respect Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (INCI) is known to be very aggressive; for reasons of comparison it even is used as a standard irritant in skin tolerance tests of cleansing products.
The advertising messages for cleansing products often are non-specific in terms of product description. A multitude of denominations is circulating. In order to classify the different products with fantasy names it is recommended remembering the INCI codes of specific components and pay attention to their sequence on the labels (≥ 1% going by decreasing concentration, < 1% no stringent order). It takes some practice but then the products can be well rated in terms of suitability and efficacy.
Treatment routines
The above-mentioned cleansing products are used as such or integrated into more complex treatment routines in beauty institutes and medical centres. In these treatments they are applied for pre-cleansings after which more intense (deep-pore) cleansings, a specific conditioning or a regeneration supporting treatment will follow.
The treatments are adapted to the individual condition of the (problem) skin and, where necessary, to the particular requirements of customers and patients. In cases where subsequent treatments are planned, the initially used cleansing products should not contain re-fattening substances such as adhesive siloxanes or surface-active substances with dominant lipid moieties as they will interfere with the following routine.
Skin cleansing frequently is followed by a blackhead and comedo treatment ("thorough cleansing“), often with the help of vaporizers (Vapozon) and/or disinfecting alcoholic lotions. Disinfection after skin cleansings also is a significant step to prepare the skin for the meanwhile rather popular Dermal Needling treatment regardless of whether short (cosmetic purposes) or long needles (dermatological purposes) are used. Aqueous polyhexamethylene biguanide solutions (PHMB) have proved successful as disinfection agents. PHMB attacks bacteria and viruses with its cationic structure analogous to the endogenous antimicrobial peptides (AMP). In this context we also speak of an AMP booster. Further disinfecting agents without sensitising potential are 70% (V/V) alcohol and isopropyl (with similar water content).
Peelings
Exfoliating scrubs to peel off parts of the stratum corneum and not only loose skin scales also are administered after a previous skin cleansing. The most important peeling procedures are as follows:
- Mechanical peelings with water-resistant scrubbing agents – preferably made of degradable wax beads. Synthetic polymers (PE; PP, PUR) are on the decline due to the discussions around microplastics. (Sea)Salt peelings are administered in combination with herbal oils; they are advantageous insofar as the salt can be rinsed off with water after the peelings.
- Enzyme peelings contain proteases, mostly bromelain and papain; both of them dissolve the peptide bonds of the topical keratin (keratolysis). Also lipases that cleave the esters of fatty acids are used for this particular type of peeling.
- Chemical peelings with keratolytic effects based on alpha hydroxy acids (AHA) such as glycolic acid and lactic acid (in cosmetic applications), or trichloroacetic acid and phenolic compounds (in dermatological applications). The effects of herbal peelings can be compared to those of analogous chemical agents gained from natural extracts such as willow bark. Sometimes AHA acids already are added to the cleansing gels.
- Microdermabrasion is an instrument-based mechanical peeling procedure in which ultrafine particles made of quartz, aluminium oxide or similar materials are blown onto the skin through a nozzle ("sand blasting“).
- Dermabrasion by means of aqueous liquids squeezed out of a high pressure tool ("water jet treatment“).
The peeling treatment is associated with the concept of stimulating an intense regeneration of the skin with “anti-aging” effects. Long-term observations however point to an increased susceptibility for rosacea and perioral dermatitis after long and repeated intense chemical peelings with fruit acids, in particular in the case of very light skin. As in many other cases, it can be stated that excess skin care measures have counterproductive effects.
Light peelings can be obtained with healing earth masks. In general, masks are used to optimise cleansing treatments (“cleansing masks”). Besides healing earth also kaolin, zeolites and even activated carbon are used to absorb substances from the skin.
Adverse effects
Each cleansing procedure leaves traces in the skin barrier and skin flora. Without applying appropriate skin care preparations after such treatments the skin tends to dehydrate since the TEWL is increased and natural moisturizing substances have been eliminated. Also the susceptibility towards influences of external substances (originating from environment, work and household) and sun radiation is increased. The more intense the cleansing and the more preservatives and disinfectant agents are involved the more the skin flora alias microbiome will suffer. Accordingly, the acid mantle becomes weaker and infections will be facilitated. These mechanisms should be kept in mind when selecting the cleansing agents and the frequency of application.
The pH values of the cleansing agents can be neutral to slightly acidic. If buffer substances (phosphates, citrates etc.) are contained in higher dosage, a pH value of 5.5 should be targeted. In case that only a small quantity or no buffer substances at all are contained, the pH of the preparations can be neglected since the buffer capacity of the skin will adjust to the physiological value in no time. Alkaline cleansing preparations have an irritant effect due to the eliminated acid mantle, a condition to which the skin reacts with an increased formation of barrier components. With a low regenerative capacity of the skin, as occurs in the case of atopic skin, such preparations are not recommended.
Literature:
Lautenschläger H, Die Haut und ihre Pflege – Physiologie und Chemie im Einklang? Chemie in unserer Zeit 2021, 55 (5), 306-319; Copyright © 2021 Wiley-VCH GmbH; Reproduced with permission.
Lautenschläger H, Gesichtsreinigung – Inhaltsstoffe & Geräte, medical Beauty Forum 2018 (1), 14-17
Dr Hans Lautenschläger
|

