Of course make-up is the first choice to consider when it comes to intensify the natural skin tone. A countless number of people however prefer a longer lasting tan without the efforts of daily renewal and that is why they favor self-tanning products.
Sweet tanning with DHA
The longest known and still most popular agent is dihydroxyacetone (DHA) with the empirical formula C3H6O3 (structural formula shown in fig.1). It belongs to the substance class of carbohydrates and has a sweet taste and related herewith also is the story of its discovery. In the fifties it has been tested as a product for the oral diagnosis of glycogenosis. As a side effect brown spots around the mouth developed and this was the reason for its later use in self-tanning products. 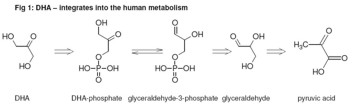 Maillard reaction - a common phenomenon
DHA reacts with the amino groups of the superficial corneocyte proteins, i.e. a complicated condensation (a chemical condensing reaction with elimination of water) that pertains to the specific Maillard reactions. Although unconscious and mechanical, Maillard reactions belong to the every-day life of a housewife as they occur during the baking and roasting process and are responsible for the brown color. In case of DHA we speak of a melanoidin formation.
DHA is inexpensive, non-toxic and in form of dihydroxyaceton phosphate it is a component of the human metabolism. There it is balanced with the glyceraldehyd-3-phosphate which integrates into the citric acid cycle after oxidation to pyruvic acid and finally is exhaled as carbon dioxide. In the human body DHA phosphate is formed after the hydrolysis of fructose-1.6-diphosphate. That is why any question referring to a toxicity of today's full body sprays with regard to the DHA dose can be answered in the negative. Any problems which may show up can rather be related to the different additives used. The fact that minor amounts of formaldehyde may form in specific circumstances like e.g. storage in bright sun light may rather be insignificant with regard to toxicology and allergology. Just like the DHA these small amounts react with the proteins and amino acids in the horny layer.
DHA is used in O/W emulsions in concentrations between 2 to 10 per cent however mostly between 2 to 5 per cent. High concentrations have stronger tanning effects however frequently produce irregular tanning which occurs due to the varying distribution of loosely tied corneocytes, locally varying skin roughness and also due to the thickness of the skin. This is why knees, elbows and ankles often show spots of different tanning intensity. As a general rule it can be said that the thicker the horny layer the more intense the tanning. So it is quite important to have well spreading or low-viscosity products.
Long-lasting effects - by way of comparison
A little more patience is necessary when lower DHA concentrations are used however the result generally is a rather flawless and perfect tan. Tanning starts about one hour after application and shows its maximum effect after 8 to 24 hours. If tanning effects are expected to show right after the application, pigments can be added to the products. The DHA tanning will last for about one week unless there has been an additional application in the meantime. A peeling is generally recommended in order to avoid streaky tanning and spots.
Vitiligo, spider veins and co.
An important field of application for self-tanning products is vitiligo, the skin disease with its symptomatic white spots on the skin. In this specific case particularly the melanin-free skin parts are treated while a whitening concentrate is applied on the pigment-containing parts of the skin in order to balance the different skin tones. The melanoidin which forms on the skin surface provides very little UV-A protection on the skin only, or in other words, an estimated SPF of 3, and no protection at all against UV-B radiation. The tanning effect highly depends on the natural skin tone, i.e. a skin with a bronze-colored base tone (carotene) generates the best effects while pale and rosy skin tones show less favorable results.
An important field of application for self-tanning products also is the covering of spider veins and other visible tiny veins. In this case additional green pigments of the make-up can neutralize the red tones. Also individuals with hyperpigmentation may benefit from self-tanning products as the variations in their skin tones can be softened.
Erythrulose - frequently used in combination with DHA
Besides DHA erythrulose is also used often even in combination with DHA. Just like DHA, erythrulose is a carbohydrate (tetrose = monosaccharide with 4 C-atoms) with the empirical formula C4H8O4 (structural formula see fig. 2). Like DHA the substance reacts to form an analogous melanoidin. The skin tone has a slightly reddish tint and fades off faster than DHA induced tans. 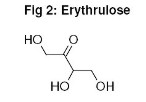
Tanning boosters
During the past years the cosmetic industry increasingly worked with substances involved in the natural melanin formation. The advantages here are pretty obvious. Unlike the melanoidin process a natural tan is induced and protection against UV radiation also is provided.
It is a well-known fact that the enzyme tyrosinase transforms the amino acid tyrosine into dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) and into its quinoid form, the DOPA quinone (structural formulas see fig. 3) which is the base for the formation of both the melanin types eumelanin (dark brown) and pheomelanin (reddish yellow). The combination of both the types is responsible for the skin tone which varies from skin to skin. 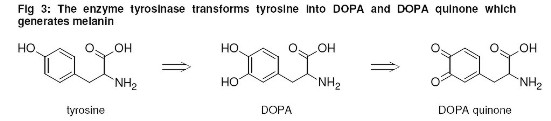 The tyrosinase is controlled by UV radiation and induced by the α-melanocytes stimulating hormone (α-MSH). Further tyrosinase stimulators are the β-endorphins. Endorphin related substances can be found in specific vegetable extracts as e.g. the chaste berry or chaste tree (vitex agnus castus) and together with synthetic acetyl tyrosine, a tyrosine prodrug (structural formula see fig. 4), they are able to induce the UV independent formation of melanin. Additional UV radiation will speed up and stimulate the melanin formation process after the product has been applied. New developments concentrate on additional tyrosinase activators and adequate transport systems to integrate the substances into the skin. 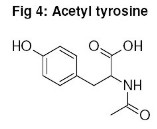 Carotene and Vitamin A
The knowledge that carrots influence the natural skin tone already dates back to grandma's times. Although this effect is limited even if appropriate dietary supplements are used, it may be another piece in the jigsaw puzzle of indicators for a healthy skin appearance. It should however be mentioned that pure β-carotene has to be supplied in relatively high dosage on a long-term base in order to achieve measurable protective effects. According to studies a SPF between 2 and 3 may be gained though. Similar effects are reported of a high daily dosage of tomato puree. Tomatoes contain the red pigment lycopin which also improves the protection against UV radiation and like carotene it belongs to the carotinoids.
In this context however it may be asked whether vitamin A which is formed from carotene in the human body also influences the skin tanning process. Even in combination with carrier systems like nanoparticles however the question can be answered in the negative.
Further natural tanning substances
Juglon with the chemical denomination 5-hydroxy-1.4-naphthoquinone (see fig. 5) is extracted from the green walnut shells. Related to this substance is 2-hydroxy-1.4-naphthoquinone (isomer, fig. 5) extracted from henna leaves, which also has been known as a coloring agent for a very long time. 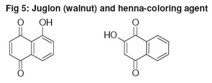 Both the extracts show brownish tanning effects which however neither achieve the intensity of DHA nor provide any protection against UV-radiation. In addition to that also substances of the tannin group are sometimes used. Their significance in this field however is negligible. Dr. Hans Lautenschläger | 
